Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, obesity and metabolism
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score as a Sensitive Indicator of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Long-Term Cohort Study
- Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Sang Min Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Rae Cho, Young-Hoon Jeong, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2023;38(5):568-577. Published online October 10, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2023.1770

- 1,545 View
- 113 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) has become an important tool for evaluating cardiovascular disease (CVD). This study evaluated the significance of CACS for future CVD through more than 10 years of follow-up in asymptomatic Korean populations with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) known to have a relatively low CACS burden.
Methods
We enrolled 981 asymptomatic T2DM patients without CVD at baseline who underwent CACS evaluation using multidetector computed tomography between January 2008 and December 2014. They were grouped into five predefined CACS categories based on Agatston scores and followed up by August 2020. The primary endpoint was incident CVD events, including coronary, cerebrovascular, and peripheral arterial disease.
Results
The relative risk of CVD was significantly higher in patients with CACS ≥10, and the significance persisted after adjustment for known confounders. A higher CACS category indicated a higher incidence of future CVD: hazard ratio (95% confidence interval) 4.09 (1.79 to 9.36), 12.00 (5.61 to 25.69), and 38.79 (16.43 to 91.59) for 10≤ CACS <100, 100≤ CACS <400, and CACS ≥400, respectively. During the 12-year follow-up period, the difference in event-free survival more than doubled as the category increased. Patients with CACS below 10 had very low CVD incidence throughout the follow-up. The receiver operating characteristic analysis showed better area under curve when the CACS cutoff was 10 than 100.
Conclusion
CACS can be a sensitive marker of CVD risk. Specifically, CACS above 10 is an indicator of CVD high-risk requiring more intensive medical treatment in Koreans with T2DM.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Comparative Study of Ex Vivo Antiplatelet Activity of Aspirin and Cilostazol in Patients with Diabetes and High Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
- Sangmo Hong, Woo Je Lee, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):233-242. Published online April 6, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1353
- 3,808 View
- 166 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The role of aspirin in primary cardiovascular disease prevention in patients with diabetes remains controversial. However, some studies have suggested beneficial effects of cilostazol on cardiovascular disease in patients with diabetes. We prospectively investigated the antiplatelet effects of cilostazol compared with aspirin in patients with diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors.
Methods
We randomly assigned 116 patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors but no evident cardiovascular disease to receive aspirin at a dose of 100 mg or cilostazol at a dose of 200 mg daily for 14 days. The primary efficacy outcome was antiplatelet effects of aspirin and cilostazol assessed with the VerifyNow system (aspirin response units [ARU]) and PFA-100 (closure time [CT]). Secondary outcomes were changes of clinical laboratory data (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02933788).
Results
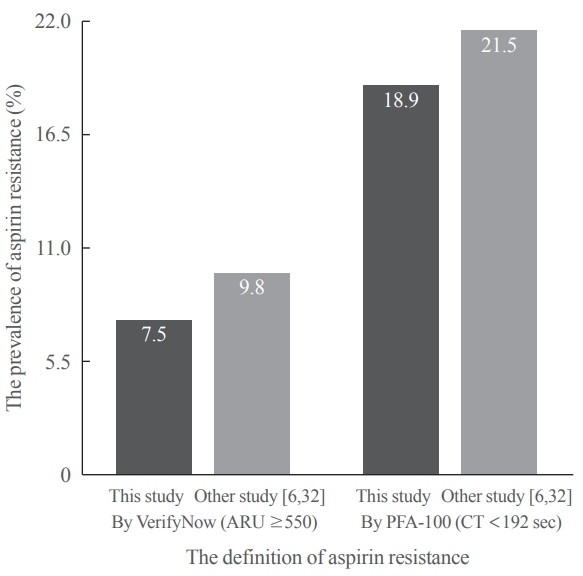
After 14 days, there was greater decrease in ARU in aspirin (–28.9%±9.9%) compared cilostazol (–0.4%±7.1%, P<0.001) and was greater increase in CT in aspirin (99.6%±63.5%) compared cilostazol (25.7%±54.1%, P<0.001). The prevalence of aspirin resistance was 7.5% according to VerifyNow (defined by ARU ≥550) and 18.9% according to PFA-100 (CT <192 seconds). Compared with aspirin, cilostazol treatment was associated with increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (7.1%±12.7% vs. 4.2%±18.0%, P=0.006) and decreased triglycerides (–9.4%±33.7% vs. 4.4%±17.57%, P=0.016). However, there were no significant changes in total and low density lipoprotein cholesterol, C-reactive protein level, and cluster of differentiation 40 ligand between cilostazol and aspirin groups.
Conclusion
Aspirin showed better antiplatelet effects assessed with VerifyNow and PFA-100 compared with cilostazol. However, there were favorable changes in atherogenic dyslipidemia only in the cilostazol.

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):628-636. Published online May 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.948
- 5,801 View
- 170 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the clinical characteristics of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in Korea, using a nationwide database.
Methods
We analyzed 417,139 women who gave birth between 2011 and 2015 using the Korean National Health Information Database. They underwent the Korean National Health Screening Program within one year before pregnancy and were not prescribed drugs for diabetes nor diagnosed with diabetes mellitus before 280 days antepartum. Patients with GDM were defined as those who visited the outpatient clinic more than twice with GDM codes.
Results
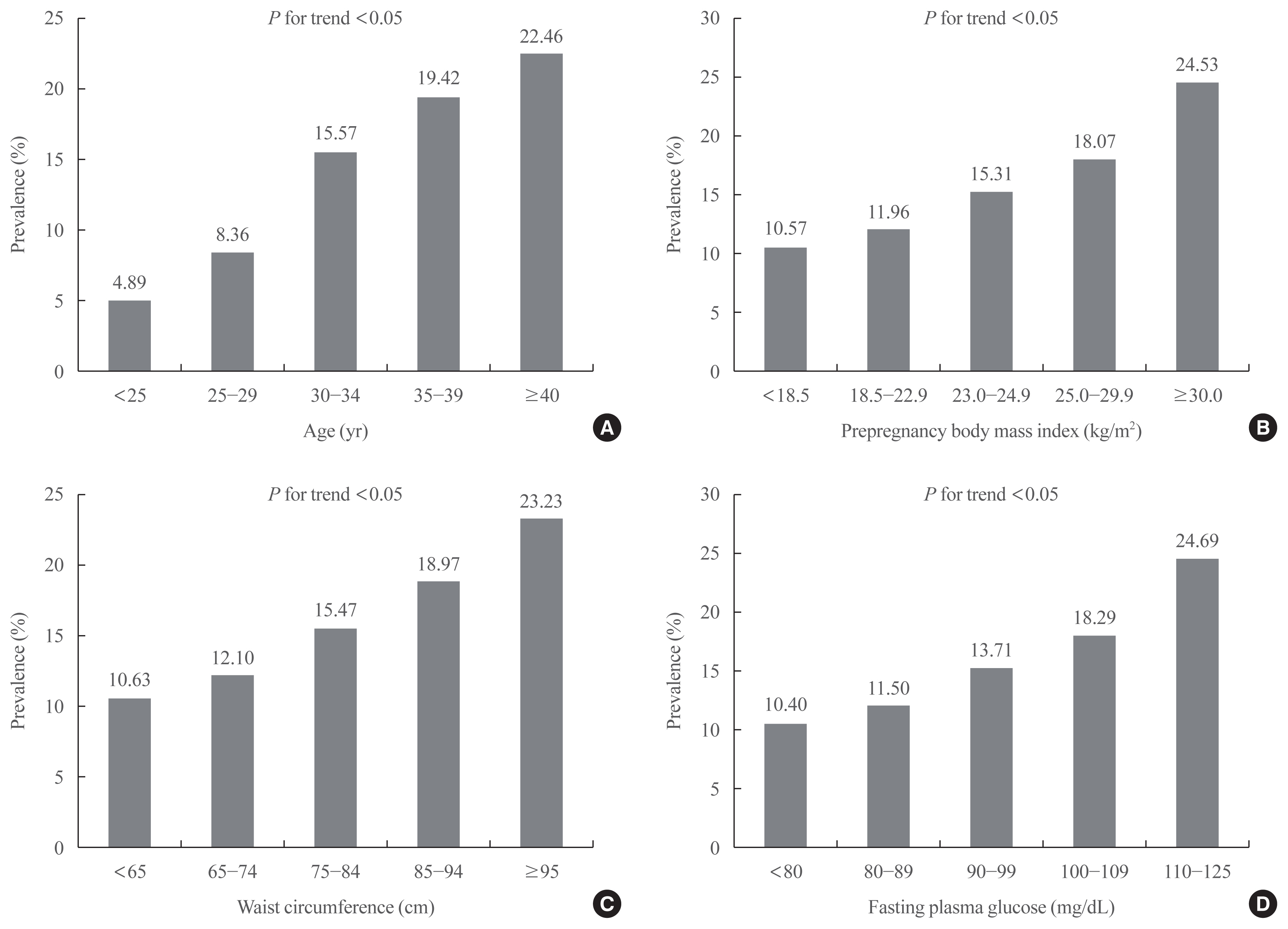
The prevalence of GDM was 12.70% and increased with increasing maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) (P for trend <0.05). As compared with those aged <25 years, the odds ratio for women with GDM aged ≥40 years were 4.804 (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.436 to 5.203) after adjustment for covariates. Women with prepregnancy BMI ≥30 kg/m2 were at 1.898 times (95% CI, 1.736 to 2.075) greater risk for GDM than those with prepregnancy BMI <18.5 kg/m2. Women with WC of ≥95 cm were at 1.158 times (95% CI, 1.029 to 1.191) greater risk for GDM than women with WC of less than 65 cm. High FPG, high income, smoking, and drinking were associated with an elevated risk of GDM.
Conclusion
The prevalence of GDM in Korean women increased up to 12.70% during 2011 to 2015. These data suggest the importance of GDM screening and prevention in high-risk groups in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationships between triglyceride-glucose index and incident gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study of a Korean population using publicly available data
Zihe Mo, Changchun Cao, Yong Han, Haofei Hu, Yongcheng He, Xin Zuo
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose tolerance test with a single abnormal value as a predictor of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a multicenter retrospective study
Seon Ui Lee, Subeen Hong, Sae Kyung Choi, Su Mi Kim, Jae Eun Shin, Ki Cheol Kil, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Ha Wie, Yun Sung Jo, Hyun Sun Ko
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploring the influence of microbiota on gestational diabetes and its potential as a biomarker
Suresh Bokoliya, Stephanie McClellan, Yanjiao Zhou, Nini Fan
Frontiers in Bacteriology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum afamin levels in predicting gestational diabetes mellitus and preeclampsia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ying Yuan, Wenyin He, Xuejiao Fan, Junyu Liang, Zhen Cao, Lei Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smoking during pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Kleoniki I. Athanasiadou, Stavroula A. Paschou, Evgenia Papakonstantinou, Vasiliki Vasileiou, Fotini Kanouta, Paraskevi Kazakou, Katerina Stefanaki, Georgia N. Kassi, Theodora Psaltopoulou, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Eleni Anastasiou
Endocrine.2023; 82(2): 250. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a second analysis based on data from a prospective cohort study
Yun You, Haofei Hu, Changchun Cao, Yong Han, Jie Tang, Weihua Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Maternal Gestational Diabetes Influences DNA Methylation in the Serotonin System in the Human Placenta
Jae Yen Song, Kyung Eun Lee, Eun Jeong Byeon, Jieun Choi, Sa Jin Kim, Jae Eun Shin
Life.2022; 12(11): 1869. CrossRef - Fetal Abdominal Obesity Detected At 24 to 28 Weeks of Gestation Persists Until Delivery Despite Management of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:547-57)
Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 966. CrossRef
- Relationships between triglyceride-glucose index and incident gestational diabetes mellitus: a prospective cohort study of a Korean population using publicly available data

- Clinical Study
- Serum Transferrin Predicts New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes in Koreans: A 4-Year Retrospective Longitudinal Study
- Jong Dai Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, Keun-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):610-617. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.721
- 4,393 View
- 98 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
It is well known that high serum ferritin, a marker of iron storage, predicts incident type 2 diabetes. Limited information is available on the association between transferrin, another marker of iron metabolism, and type 2 diabetes. Thus, we investigated the association between transferrin and incident type 2 diabetes.
Methods
Total 31,717 participants (mean age, 40.4±7.2 years) in a health screening program in 2005 were assessed via cross-sectional analysis. We included 30,699 subjects who underwent medical check-up in 2005 and 2009 and did not have type 2 diabetes at baseline in this retrospective longitudinal analysis.
Results
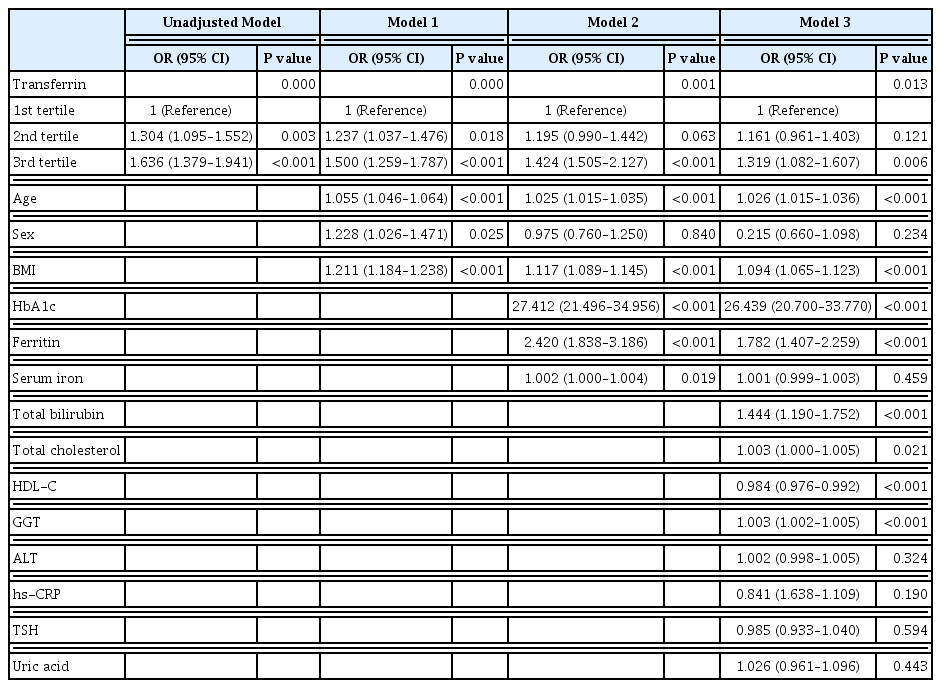
The serum transferrin level was higher in the type 2 diabetes group than in the non-type 2 diabetes group (58.32±7.74 μmol/L vs. 56.17±7.96 μmol/L, P<0.001). Transferrin correlated with fasting serum glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin in the correlational analysis (r=0.062, P<0.001 and r=0.077, P<0.001, respectively) after full adjustment for covariates. Transferrin was more closely related to homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance than to homeostasis model assessment of β cell function (r=0.042, P<0.001 and r=–0.019, P=0.004, respectively) after full adjustment. Transferrin predicted incident type 2 diabetes in non-type 2 diabetic subjects in a multivariate linear regression analysis; the odds ratio (95% confidence interval [CI]) of the 3rd tertile compared to that in the 1st tertile of transferrin for incident diabetes was 1.319 (95% CI, 1.082 to 1.607) after full adjustment (P=0.006).
Conclusion
Transferrin is positively associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes
Xingyue Wang, You Wang, Junjie Hou, Hongyang Liu, Rong Zeng, Xiangyu Li, Mei Han, Qingrun Li, Linong Ji, Desi Pan, Weiping Jia, Wen Zhong, Tao Xu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Proteomic Signature of Endometrial Cancer in Patients with Diabetes
Muhammad Mujammami, Mohamed Rafiullah, Khalid Akkour, Assim A. Alfadda, Afshan Masood, Salini Scaria Joy, Hani Alhalal, Maria Arafah, Eman Alshehri, Ibrahim O. Alanazi, Hicham Benabdelkamel
ACS Omega.2024; 9(4): 4721. CrossRef - Association between systemic iron status and β-cell function and insulin sensitivity in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Yao Qin, Yiting Huang, Yuxiao Li, Lu Qin, Qianying Wei, Xin Chen, Chuanhui Yang, Mei Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Serum Level of Ceruloplasmin, Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and Transferrin as Markers of Severity in SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Patricia-Andrada Reștea, Ștefan Țigan, Laura Grațiela Vicaș, Luminița Fritea, Eleonora Marian, Tunde Jurca, Annamaria Pallag, Iulius Liviu Mureșan, Corina Moisa, Otilia Micle, Mariana Eugenia Mureșan
Microbiology Research.2023; 14(4): 1670. CrossRef
- Plasma proteome profiling reveals the therapeutic effects of the PPAR pan-agonist chiglitazar on insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism, and inflammation in type 2 diabetes

- Clinical Study
- Serum Adiponectin and Progranulin Level in Patients with Benign Thyroid Nodule or Papillary Thyroid Cancer
- Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Ji-Sup Yun, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):396-406. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.396

- 5,637 View
- 108 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is associated with thyroid cancer risk. Adiponectin has insulin-sensitizing and anti-inflammatory effects, while progranulin is associated with inflammation and tumorigenesis. We investigated serum adiponectin and progranulin levels in patients with benign thyroid nodule (benign group) and papillary thyroid cancer (PTC; PTC group). The associations between these levels and the clinicopathological features of PTC were evaluated.
Methods
We included 157 patients who underwent thyroid surgery (17% of benign and 83% of PTC group). Clinicopathological features including size, lymph node metastasis, extrathyroidal extension (ETE), multifocality, American Thyroid Association risk stratification were evaluated.
Results
The age was 42.0 years, and 69% were female. Serum adiponectin and progranulin levels were 6.3 μg/mL and 101.5 ng/mL in the benign group and 5.4 μg/mL and 106.1 ng/mL in the PTC group, respectively (P=0.6 and P=0.4, respectively). Serum adiponectin levels showed no significant differences according to clinicopathological features of PTC. The proportions of patients with primary tumor size >1 cm were 3%, 5%, 8%, and 8% according to serum progranulin level quartiles, respectively (P=0.03). The proportions of patients with microscopic/gross ETE were 8%/0%, 9%/1%, 11%/1%, and 11%/2% according to serum progranulin level quartiles, respectively. Median serum progranulin level was significantly higher in patients with PTC >1 cm than in patients with papillary thyroid microcarcinoma (P=0.04, 115.3 ng/mL and 104.7 ng/mL, respectively).
Conclusion
Serum adiponectin and progranulin levels showed no significant difference between benign and PTC groups. Increased serum progranulin levels were significantly associated with PTC >1 cm and microscopic and gross ETE. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring the logic and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of AdipoRon-based adiponectin replacement therapy against hormone-related cancers—a systematic review
Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Andreline Franchi Sosin, Caroline Barbalho Lamas, Ricardo de Alvares Goulart, Jesselina Francisco dos Santos Haber, Claudia Rucco Penteado Detregiachi, Sandra Maria Barbalho
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2024; 397(4): 2067. CrossRef - Adiponectin Inhibits the Progression of Obesity-Associated Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Through Autophagy
Changlin Li, Jiao Zhang, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Nan Liang, Haixia Guan, Hui Sun
Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Progranulin Oncogenic Network in Solid Tumors
Elisa Ventura, Giacomo Ducci, Reyes Benot Dominguez, Valentina Ruggiero, Antonino Belfiore, Elena Sacco, Marco Vanoni, Renato V. Iozzo, Antonio Giordano, Andrea Morrione
Cancers.2023; 15(6): 1706. CrossRef - Obesity and thyroid cancer risk
Lauren C. Burrage, Donald S.A. McLeod, Susan J. Jordan
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(5): 244. CrossRef - Progranulin promoted the proliferation, metastasis, and suppressed apoptosis via JAK2-STAT3/4 signaling pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma
Yanxu Dong, Hao Tan, Lidong Wang, Zhen Liu
Cancer Cell International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and Thyroid Cancer Risk: An Update
Fabiana Franchini, Giuseppe Palatucci, Annamaria Colao, Paola Ungaro, Paolo Emidio Macchia, Immacolata Cristina Nettore
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(3): 1116. CrossRef - Obesity and Overweight Are Associated with Minimal Extrathyroidal Extension, Multifocality and Bilaterality of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Dorota Diakowska, Marta Rzeszutko, Jerzy Rudnicki
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(5): 970. CrossRef - Adiponectin and Thyroid Cancer: Insight into the Association between Adiponectin and Obesity
Yuanyuan Zhou, Ying Yang, Taicheng Zhou, Bai Li, Zhanjian Wang
Aging and disease.2021; 12(2): 597. CrossRef
- Exploring the logic and conducting a comprehensive evaluation of AdipoRon-based adiponectin replacement therapy against hormone-related cancers—a systematic review

- Endocrine Research
- Deficiency of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Reduces the Expression of Prohibitin and Causes β-Cell Impairment via Mitochondrial Dysregulation
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(3):403-412. Published online September 18, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.3.403
- 4,204 View
- 50 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Emerging evidence suggests that sphingolipids may be involved in type 2 diabetes. However, the exact signaling defect through which disordered sphingolipid metabolism induces β-cell dysfunction remains unknown. The current study demonstrated that sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), the product of sphingosine kinase (SphK), is an essential factor for maintaining β-cell function and survival via regulation of mitochondrial action, as mediated by prohibitin (PHB).
Methods We examined β-cell function and viability, as measured by mitochondrial function, in mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells in response to manipulation of cellular S1P and PHB levels.
Results Lack of S1P induced by sphingosine kinase inhibitor (SphKi) treatment caused β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis, with repression of mitochondrial function shown by decreases in cellular adenosine triphosphate content, the oxygen consumption rate, the expression of oxidative phosphorylation complexes, the mitochondrial membrane potential, and the expression of key regulators of mitochondrial dynamics (mitochondrial dynamin-like GTPase [OPA1] and mitofusin 1 [MFN1]). Supplementation of S1P led to the recovery of mitochondrial function and greatly improved β-cell function and viability. Knockdown of SphK2 using small interfering RNA induced mitochondrial dysfunction, decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS), and reduced the expression of PHB, an essential regulator of mitochondrial metabolism. PHB deficiency significantly reduced GSIS and induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and co-treatment with S1P did not reverse these trends.
Conclusion Altogether, these data suggest that S1P is an essential factor in the maintenance of β-cell function and survival through its regulation of mitochondrial action and PHB expression.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial Cristae Morphology Reflecting Metabolism, Superoxide Formation, Redox Homeostasis, and Pathology
Petr Ježek, Martin Jabůrek, Blanka Holendová, Hana Engstová, Andrea Dlasková
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2023; 39(10-12): 635. CrossRef - Sphingolipids in mitochondria—from function to disease
Maryam Jamil, Lauren Ashley Cowart
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate in mitochondrial function and metabolic diseases
Meng Duan, Pan Gao, Sheng‐xi Chen, Petr Novák, Kai Yin, Xiao Zhu
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Involvement of miR‐27a‐3p in diabetic nephropathy via affecting renal fibrosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum stress
Lina Wu, Qingzhu Wang, Feng Guo, Xiaojun Ma, Jiao Wang, Yanyan Zhao, Yushan Yan, Guijun Qin
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2021; 236(2): 1454. CrossRef - Sphingosine‐1‐phosphate in acute exercise and training
Katarzyna Hodun, Adrian Chabowski, Marcin Baranowski
Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports.2021; 31(5): 945. CrossRef - The Ethyl Acetate Extract From Celastrus orbiculatus Promotes Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Mitochondria Regulation by PHB
Lide Tao, Zixin Yin, Tengyang Ni, Zewen Chu, Shihua Hao, Zeyu Wang, Masataka Sunagawa, Haibo Wang, Yanqing Liu
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine 1-phosphate Stimulates Insulin Secretion and Improves Cell Survival by Blocking Voltage-dependent K+ Channels in β Cells
Zhihong Liu, Huanhuan Yang, Linping Zhi, Huan Xue, Zhihong Lu, Yanli Zhao, Lijuan Cui, Tao Liu, Shouan Ren, Peifeng He, Yunfeng Liu, Yi Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Lyase Regulates Sensitivity of Pancreatic Beta-Cells to Lipotoxicity
Yadi Tang, Thomas Plötz, Markus H. Gräler, Ewa Gurgul-Convey
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10893. CrossRef - Sphingolipids and Mitochondrial Dynamic
Lais Brigliadori Fugio, Fernanda B. Coeli-Lacchini, Andréia Machado Leopoldino
Cells.2020; 9(3): 581. CrossRef - Diminished Sphingolipid Metabolism, a Hallmark of Future Type 2 Diabetes Pathogenesis, Is Linked to Pancreatic β Cell Dysfunction
Saifur R. Khan, Yousef Manialawy, Andreea Obersterescu, Brian J. Cox, Erica P. Gunderson, Michael B. Wheeler
iScience.2020; 23(10): 101566. CrossRef - Neuronal Metabolism and Neuroprotection: Neuroprotective Effect of Fingolimod on Menadione-Induced Mitochondrial Damage
Antonio Gil, Elisa Martín-Montañez, Nadia Valverde, Estrella Lara, Federica Boraldi, Silvia Claros, Silvana-Yanina Romero-Zerbo, Oscar Fernández, Jose Pavia, Maria Garcia-Fernandez
Cells.2020; 10(1): 34. CrossRef - WITHDRAWN: Ceramide and Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in adipose dysfunction
Zijian Fang, Susan Pyne, Nigel J. Pyne
Progress in Lipid Research.2019; : 100991. CrossRef - Dynamic of mitochondrial network, cristae, and mitochondrial nucleoids in pancreatic β-cells
Petr Ježek, Andrea Dlasková
Mitochondrion.2019; 49: 245. CrossRef - Sphingosine kinase 1 overexpression induces MFN2 fragmentation and alters mitochondrial matrix Ca2+ handling in HeLa cells
I. Pulli, C. Löf, T. Blom, M.Y. Asghar, T. Lassila, N. Bäck, K.-L. Lin, J.H. Nyström, K. Kemppainen, D.M. Toivola, E. Dufour, A. Sanz, H.M. Cooper, J.B. Parys, K. Törnquist
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2019; 1866(9): 1475. CrossRef - Ceramide and sphingosine 1-phosphate in adipose dysfunction
Zijian Fang, Susan Pyne, Nigel J. Pyne
Progress in Lipid Research.2019; 74: 145. CrossRef - S1P/S1P Receptor Signaling in Neuromuscolar Disorders
Elisabetta Meacci, Mercedes Garcia-Gil
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(24): 6364. CrossRef
- Mitochondrial Cristae Morphology Reflecting Metabolism, Superoxide Formation, Redox Homeostasis, and Pathology

- Diabetes
- Pioglitazone Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Inflammation and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Pancreatic β-Cells
- Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):105-113. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.105
- 6,244 View
- 96 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activator gamma (PPARγ) is a useful therapeutic target for obesity and diabetes, but its role in protecting β-cell function and viability is unclear.
Methods To identify the potential functions of PPARγ in β-cells, we treated mouse insulinoma 6 (MIN6) cells with the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone in conditions of lipotoxicity, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and inflammation.
Results Palmitate-treated cells incubated with pioglitazone exhibited significant improvements in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and the repression of apoptosis, as shown by decreased caspase-3 cleavage and poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerase activity. Pioglitazone also reversed the palmitate-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 6 [IL-6], and IL-1β) and ER stress markers (phosphor-eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α, glucose-regulated protein 78 [GRP78], cleaved-activating transcription factor 6 [ATF6], and C/EBP homologous protein [CHOP]), and pioglitazone significantly attenuated inflammation and ER stress in lipopolysaccharide- or tunicamycin-treated MIN6 cells. The protective effect of pioglitazone was also tested in pancreatic islets from high-fat-fed KK-Ay mice administered 0.02% (wt/wt) pioglitazone or vehicle for 6 weeks. Pioglitazone remarkably reduced the expression of ATF6α, GRP78, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, prevented α-cell infiltration into the pancreatic islets, and upregulated glucose transporter 2 (Glut2) expression in β-cells. Moreover, the preservation of β-cells by pioglitazone was accompanied by a significant reduction of blood glucose levels.
Conclusion Altogether, these results support the proposal that PPARγ agonists not only suppress insulin resistance, but also prevent β-cell impairment via protection against ER stress and inflammation. The activation of PPARγ might be a new therapeutic approach for improving β-cell survival and insulin secretion in patients with diabetes mellitus
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s
Nancy Ahuja, Shalini Gupta, Rashmi Arora, Ella Bhagyaraj, Drishti Tiwari, Sumit Kumar, Pawan Gupta
Life Science Alliance.2024; 7(7): e202302416. CrossRef - Prosthetic vascular grafts engineered to combat calcification: Progress and future directions
Taylor K. Brown, Sara Alharbi, Karen J. Ho, Bin Jiang
Biotechnology and Bioengineering.2023; 120(4): 953. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes mellitus, and cardiometabolic risk: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2023
Harold Edward Bays, Shagun Bindlish, Tiffany Lowe Clayton
Obesity Pillars.2023; 5: 100056. CrossRef - Metformin promotes osteogenic differentiation and prevents hyperglycaemia-induced osteoporosis by suppressing PPARγ expression
Lifeng Zheng, Ximei Shen, Yun Xie, Hong Lian, Sunjie Yan, Shizhong Wang
Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.2023; 55(3): 394. CrossRef - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors as targets to treat metabolic diseases: Focus on the adipose tissue, liver, and pancreas
Henrique Souza-Tavares, Carolline Santos Miranda, Isabela Macedo Lopes Vasques-Monteiro, Cristian Sandoval, Daiana Araujo Santana-Oliveira, Flavia Maria Silva-Veiga, Aline Fernandes-da-Silva, Vanessa Souza-Mello
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 29(26): 4136. CrossRef - Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase upregulation contributes to palmitate-elicited peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor transactivation in hepatocytes
Qing Song, Jun Wang, Alexandra Griffiths, Samuel Man Lee, Iredia D. Iyamu, Rong Huang, Jose Cordoba-Chacon, Zhenyuan Song
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2023; 325(1): C29. CrossRef - The global perspective on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) in ectopic fat deposition: A review
Yanhao Qiu, Mailin Gan, Xingyu Wang, Tianci Liao, Qiuyang Chen, Yuhang Lei, Lei Chen, Jinyong Wang, Ye Zhao, Lili Niu, Yan Wang, Shunhua Zhang, Li Zhu, Linyuan Shen
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 253: 127042. CrossRef - Chemical inducer of regucalcin attenuates lipopolysaccharide‐induced inflammatory responses in pancreatic MIN6 β‐cells and RAW264.7 macrophages
Tomiyasu Murata, Kazunori Hashimoto, Susumu Kohno, Chiaki Takahashi, Masayoshi Yamaguchi, Chihiro Ito, Itoigawa Masataka, Roji Kojima, Kiyomi Hikita, Norio Kaneda
FEBS Open Bio.2022; 12(1): 175. CrossRef - Targets for rescue from fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(2): 57. CrossRef - Analysis of changes in the proteomic profile of porcine corpus luteum during different stages of the oestrous cycle: effects of PPAR gamma ligands
Zuzanna Kunicka, Karol Mierzejewski, Aleksandra Kurzyńska, Robert Stryiński, Jesús Mateos, Mónica Carrera, Monika Golubska, Iwona Bogacka, Xiaolong Wang
Reproduction, Fertility and Development.2022; 34(11): 776. CrossRef - Activation of PPARγ Protects Obese Mice from Acute Lung Injury by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis
Yin Tang, Ke Wei, Ling Liu, Jingyue Ma, Siqi Wu, Wenjing Tang, Stéphane Mandard
PPAR Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Effect of Pioglitazone on endoplasmic reticulum stress regarding in situ perfusion rat model
Vivien Telek, Luca Erlitz, Ibitamuno Caleb, Tibor Nagy, Mónika Vecsernyés, Bálint Balogh, György Sétáló, Péter Hardi, Gábor Jancsó, Ildikó Takács
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2021; 79(2): 311. CrossRef - Inflammation in Metabolic Diseases and Insulin Resistance
Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2021; 3(2): 31. CrossRef - Current Status of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Type II Diabetes
Sagir Mustapha, Mustapha Mohammed, Ahmad Khusairi Azemi, Abubakar Ibrahim Jatau, Aishatu Shehu, Lukman Mustapha, Ibrahim Muazzamu Aliyu, Rabi’u Nuhu Danraka, Abdulbasit Amin, Auwal Adam Bala, Wan Amir Nizam Wan Ahmad, Aida Hanum Ghulam Rasool, Mohd Rais M
Molecules.2021; 26(14): 4362. CrossRef - JunD Regulates Pancreatic β-Cells Function by Altering Lipid Accumulation
Kexin Wang, Yixin Cui, Peng Lin, Zhina Yao, Yu Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone even at low dosage improves NAFLD in type 2 diabetes: clinical and pathophysiological insights from a subgroup of the TOSCA.IT randomised trial
Giuseppe Della Pepa, Marco Russo, Marilena Vitale, Fabrizia Carli, Claudia Vetrani, Maria Masulli, Gabriele Riccardi, Olga Vaccaro, Amalia Gastaldelli, Angela A. Rivellese, Lutgarda Bozzetto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108984. CrossRef - Radioprotective Effect of Pioglitazone Against Genotoxicity Induced by Ionizing Radiation in Healthy Human Lymphocytes
Roya Kazemi, Seyed J. Hosseinimehr
Cardiovascular & Hematological Agents in Medicinal Chemistry .2021; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Recent Insights Into Mechanisms of β-Cell Lipo- and Glucolipotoxicity in Type 2 Diabetes
Maria Lytrivi, Anne-Laure Castell, Vincent Poitout, Miriam Cnop
Journal of Molecular Biology.2020; 432(5): 1514. CrossRef - Artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin promote β-cell apoptosis induced by palmitate via enhancing ER stress
Ke Chen, Hu Hua, Ziyang Zhu, Tong Wu, Zhanjun Jia, Qianqi Liu
Apoptosis.2020; 25(3-4): 192. CrossRef - Mechanisms of impaired pancreatic β‑cell function in high‑fat diet‑induced obese mice: The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
Xiaoqing Yi, Xuan Cai, Sisi Wang, Yanfeng Xiao
Molecular Medicine Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Docosahexaenoic and Eicosapentaenoic Acids Prevent Altered-Muc2 Secretion Induced by Palmitic Acid by Alleviating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in LS174T Goblet Cells
Quentin Escoula, Sandrine Bellenger, Michel Narce, Jérôme Bellenger
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2179. CrossRef - PPAR-γ agonist, pioglitazone, reduced oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress associated with L-NAME-induced hypertension in rats
Eman Soliman, Shereen F. Behairy, Nabila N. El-maraghy, Shimaa M. Elshazly
Life Sciences.2019; 239: 117047. CrossRef - Changes of MODY signal pathway genes in the endoplasmic reticulum stress in INS-1-3 cells
Yanan Dong, Shirui Li, Wenhui Zhao, Yanlei Wang, Tingting Ge, Jianzhong Xiao, Yukun Li, Herve Le Stunff
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0198614. CrossRef
- Nr1h4 and Thrb ameliorate ER stress and provide protection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s

- Diabetes
- The Association between Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia and the Risk of Diabetes Development: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
- Yu Hyun Kwon, Seul-Ki Kim, Jung Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2018;33(1):55-61. Published online January 30, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2018.33.1.55
- 4,167 View
- 62 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Hypertriglyceridemia is known to have an association with increased risks of insulin resistance and diabetes. The aim of this study was to investigate the risk of diabetes mellitus, according to changes in the concentrations of triglycerides, over time.
Methods A total of 15,932 non-diabetic participants (mean age 43.2 years, 68% men) who attended five consecutive annual health check-ups at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, between January 2010 and December 2014, were recruited. Participants were classified according to their triglyceride concentrations; normal (<150 mg/dL) and abnormal (≥150 mg/dL). According to the triglyceride levels in 2010 and 2012, subjects were divided into four groups: normal-normal, normal-abnormal, abnormal-normal, and abnormal-abnormal. The risk for incident diabetes was assessed in 2014.
Results Among the total subjects, 67.5% belonged to the normal-normal group, 8.6% to the normal-abnormal group, 9.4% to the abnormal-normal group, and 14.5% to the abnormal-abnormal group. A total of 234 subjects (1.5%) were newly diagnosed with diabetes, between 2010 and 2014. Over 4 years, 1%, 1.5%, 2.1%, and 3.0% of the subjects developed diabetes in the normal-normal, normal-abnormal, abnormal-normal, and abnormal-abnormal groups, respectively. When the risk for incident diabetes was analyzed in the groups, after adjusting the confounding variables, a 1.58-fold increase in the risk of diabetes (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 2.26) was observed in the participants with persistent hypertriglyceridemia (abnormal-abnormal group). This was attenuated by further adjustments for body mass index (BMI) (hazard ratio, 1.25; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.80).
Conclusion In this large study population, persistent hypertriglyceridemia, over a period of 2 years, was significantly associated with the risk of incident diabetes, which was attenuated after adjustment for BMI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Usefulness of SPISE Index for Screening and Detection of Early Stages of Insulin Resistance among Chilean Young Adults
Isabel Pereyra González, Sandra Lopez-Arana
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2023; 79(4): 372. CrossRef - Lipid variability in patients with diabetes mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(4): 126. CrossRef - Sesamin: A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Ameliorating Symptoms of Diabetes
Shu-Ming Huang, Cheng-Hung Chuang, Christine Joyce F. Rejano, Lemmuel L. Tayo, Cheng-Yang Hsieh, Steven Kuan-Hua Huang, Po-Wei Tsai
Molecules.2023; 28(21): 7255. CrossRef - Variability, Mean, and Baseline Values of Metabolic Parameters in Predicting Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Duong Duc Pham, Jaekyung Song, Yunwan Jeon, Ibrahimi Hajar, Chae Hun Leem
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): 1270. CrossRef - Lipid Variability and Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 28. CrossRef - The Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Russian Population Cohort According to Data from the HAPIEE Project
Svetlana V. Mustafina, Oksana D. Rymar, Liliya V. Shcherbakova, Evgeniy G. Verevkin, Hynek Pikhart, Olga V. Sazonova, Yuliya I. Ragino, Galina I. Simonova, Martin Bobak, Sofia K. Malyutina, Mikhail I. Voevoda
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2021; 11(2): 119. CrossRef - The influence of VDR polymorphisms on the type 2 diabetes susceptibility in Chinese: an interaction with hypertriglyceridemia
Dongdong Zhang, Cheng Cheng, Yan Wang, Yuan Xue, Yaping Liu, Yiming Liu, Mingming Feng, Ze Xu, Wenjie Li, Xing Li
Molecular Genetics and Genomics.2021; 296(4): 837. CrossRef - Development and validation of a new diabetes index for the risk classification of present and new-onset diabetes: multicohort study
Shinje Moon, Ji-Yong Jang, Yumin Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia as an Independent Predictor for Ten-Year Incidence of Diabetes in Thais
Suranut Charoensri, Supatida Turnsaket, Chatlert Pongchaiyakul
Vascular Health and Risk Management.2021; Volume 17: 519. CrossRef - Prevalence and Current Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 85. CrossRef - HDL-Cholesterol, Its Variability, and the Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(11): 5633. CrossRef - Response: The Association between Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia and the Risk of Diabetes Development: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study (Endocrinol Metab 2018;33:55–61, Yu Hyun Kwon et al.)
Eun-Jung Rhee, Yu Hyun Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(3): 425. CrossRef - The Association between Persistent Hypertriglyceridemia and the Risk of Diabetes Development: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study (Endocrinol Metab 2018;33:55–61, Yu Hyun Kwon et al.)
Mi Hae Seo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(2): 305. CrossRef
- Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults

- Clinical Study
- Changes in Body Composition According to Age and Sex among Young Non-Diabetic Korean Adults: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
- Seul-Ki Kim, Yu-Hyun Kwon, Jung Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(4):442-450. Published online November 21, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.4.442
- 6,173 View
- 63 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Age-related decreases in lean mass represent a serious health problem. We aimed to analyze the risks of rapid decreases in lean mass by age and sex in relatively young Korean adults during a 4-year follow-up study.
Methods A total of 65,856 non-diabetic participants (59.5% men, mean age 39.1 years) in a health screening program were subjected to bioimpedance body composition analyses and metabolic parameter analyses at baseline and after 4 years. The participants were sub-divided according to age, and additionally to six groups by age and the degree of body weight change over the 4-year period. The actual changes in body weight, lean mass, and fat mass and the percent changes over the 4-year period were assessed.
Results The percent change in lean mass decreased and the percent change of fat mass increased with increasing age in every age and sex group. However, the annual percent decrease in lean mass and percent increase in fat mass were significantly higher among women than among men (−0.26% vs. −0.15% and 0.34% vs. 0.42%, respectively;
P <0.01). Participants who were older than 50 years and had a weight loss <−5% during the 4 years had significantly greater decreases in lean mass and smaller decreases in fat mass, compared to those who were younger than 50 years. An odds ratio analysis to determine the lowest quartile of the percent change in lean mass according to age group revealed that participants older than 60 years had a significantly increased risk of a rapid decrease in the lean mass percentage (2.081; 95% confidence interval, 1.678 to 2.581).Conclusion Even in this relatively young study population, the lean mass decreased significantly with age, and the risk of a rapid decrease in lean mass was higher among women than among men. Furthermore, the elderly exhibited a significantly more rapid decrease in lean mass, compared with younger participants.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesity, Physical Performance, Balance Confidence, and Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results from the Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study
Ga Yang Shim, Myung Chul Yoo, Yunsoo Soh, Jinmann Chon, Chang Won Won
Nutrients.2024; 16(5): 614. CrossRef - Multisystem physiological perspective of human frailty and its modulation by physical activity
Joseph A. Taylor, Paul L. Greenhaff, David B. Bartlett, Thomas A. Jackson, Niharika A. Duggal, Janet M. Lord
Physiological Reviews.2023; 103(2): 1137. CrossRef - Partial weight reduction protocols in cats lead to better weight outcomes, compared with complete protocols, in cats with obesity
Alexander J. German, Georgiana R. T. Woods-Lee, Vincent Biourge, John Flanagan
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multifaceted effects of obesity on cancer immunotherapies: Bridging preclinical models and clinical data
Logan V. Vick, Robert J. Canter, Arta M. Monjazeb, William J. Murphy
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2023; 95: 88. CrossRef - Age-Related Trends in Body Composition among Women Aged 20–80 Years: A Cross-Sectional Study
Nirmala Rathnayake, Hasanga Rathnayake, Sarath Lekamwasam, Aron Weller
Journal of Obesity.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Increased Consumption of Unsaturated Fatty Acids Improves Body Composition in a Hypercholesterolemic Chinese Population
Sumanto Haldar, Shalini Ponnalagu, Farhana Osman, Shia Lyn Tay, Long Hui Wong, Yuan Rong Jiang, Melvin Khee Shing Leow, Christiani Jeyakumar Henry
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of a Low-cost Dairy Food Supplement with Mauritia Flexuosa (Buriti) to Combat Malnutrition: Translational Study in Mice and Institutionalized Elderly Woman
Audrey Handyara Bicalho, Fabio Ribeiro Santos, Daniele Cristina Moreira, Victor Hugo Dantas Guimarães, Guilherme Henrique Ribeiro, Alfredo Mauricio Batista De Paula, André Luis Sena Guimarães, Ulisses A. Pereira, Theles Costa, Caroline Liboreiro Paiva, Ma
Current Aging Science.2022; 15(1): 37. CrossRef - The missense variant, rs373863828, in CREBRF plays a role in longitudinal changes in body mass index in Samoans
Haoyi Fu, Nicola L. Hawley, Jenna C. Carlson, Emily M. Russell, Alysa Pomer, Hong Cheng, Take Naseri, Muagututi‘a Sefuiva Reupena, Ranjan Deka, Courtney C. Choy, Stephen T. McGarvey, Ryan L. Minster, Daniel E. Weeks
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2022; 16(3): 220. CrossRef - Relationship Between Handgrip Strength and the Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus Among Korean Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2014-2018
Sung-hyun Hong, Ji-yong Byeon, Ji-hee Min, Dong-hyuk Park, Won-hee Cho, Justin Y. Jeon
Exercise Science.2021; 30(1): 110. CrossRef - Cutoff points of adiposity anthropometric indices for low muscle mass screening in middle-aged and older healthy women
Rafaela Andrade do Nascimento, Mariana Carmem Apolinário Vieira, Rafaella Silva dos Santos Aguiar Gonçalves, Mayle Andrade Moreira, Maria Socorro Medeiros de Morais, Saionara Maria Aires da Câmara, Álvaro Campos Cavalcanti Maciel
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Edema-like symptoms are common in ultra-distance cyclists and driven by overdrinking, use of analgesics and female sex – a study of 919 athletes
Philipp Gauckler, Jana S. Kesenheimer, Andreas Kronbichler, Fiona R. Kolbinger
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of low muscle mass and associated factors in community-dwelling older adults in Singapore
Siew Ling Tey, Dieu Thi Thu Huynh, Yatin Berde, Geraldine Baggs, Choon How How, Yen Ling Low, Magdalin Cheong, Wai Leng Chow, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Samuel Teong Huang Chew
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of low skeletal muscle mass and sarcopenic obesity on albuminuria: a 7-year longitudinal study
Jee Hee Yoo, Gyuri Kim, Sung Woon Park, Min Sun Choi, Jiyeon Ahn, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Age group and gender-wise comparison of obesity indices in subjects of Varanasi
Kumar Sarvottam, Prabhat Ranjan, Umashree Yadav
Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2020; 64: 109. CrossRef - DNA Methylation in Inflammatory Pathways Modifies the Association between BMI and Adult-Onset Non-Atopic Asthma
Ayoung Jeong, Medea Imboden, Akram Ghantous, Alexei Novoloaca, Anne-Elie Carsin, Manolis Kogevinas, Christian Schindler, Gianfranco Lovison, Zdenko Herceg, Cyrille Cuenin, Roel Vermeulen, Deborah Jarvis, André Amaral, Florian Kronenberg, Paolo Vineis, Nic
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(4): 600. CrossRef - Body shape, fear of falling, physical performance, and falls among individuals aged 55 years and above
Sheng Hui Kioh, Sumaiyah Mat, Shahrul B. Kamaruzzaman, Fatimah Ibrahim, Mas Sahidayana Mokhtar, Noran N. Hairi, Robert G. Cumming, Phyo Kyaw Myint, Maw Pin Tan
European Geriatric Medicine.2019; 10(5): 801. CrossRef - Low lean tissue mass can be a predictor of one-year survival in hemodialysis patients
Aleksandra Rymarz, Julia Gibińska, Maria Zajbt, Wiesław Piechota, Stanisław Niemczyk
Renal Failure.2018; 40(1): 231. CrossRef - Relationship Between Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 7‐Year Longitudinal Study
Gyuri Kim, Seung‐Eun Lee, You‐Bin Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon‐Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1755. CrossRef - Association between abdominal obesity and increased risk for the development of hypertension regardless of physical activity: A nationwide population‐based study
Eun‐Jung Rhee, Jung‐Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se‐Eun Park, Jin‐Hyung Jung, Kyung‐Do Han, Yong‐Gyu Park, Hye Soon Park, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Soon‐Jib Yoo, Won‐Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2018; 20(10): 1417. CrossRef - Decreasing Lean Body Mass with Age: Challenges and Opportunities for Novel Therapies
Chrysoula Boutari, Christos S. Mantzoros
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(4): 422. CrossRef
- Obesity, Physical Performance, Balance Confidence, and Falls in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: Results from the Korean Frailty and Aging Cohort Study

- Clinical Study
- Waist Circumference as a Marker of Obesity Is More Predictive of Coronary Artery Calcification than Body Mass Index in Apparently Healthy Korean Adults: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
- Jongsin Park, Eun Seo Lee, Da Young Lee, Jihyun Kim, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):559-566. Published online December 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.559
- 4,553 View
- 38 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We aimed to assess the risk for coronary artery calcification (CAC) according to groups subdivided by body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) in apparently healthy Korean adults.
Methods Thirty-three thousand four hundred and thirty-two participants (mean age, 42 years) in a health screening program were divided into three groups according to BMI: <23 kg/m2 (normal), 23 to 25 kg/m2 (overweight), and >25 kg/m2 (obese). In addition, the participants were divided into two groups according to WC. Coronary artery calcium score (CACS) was measured with multi-detector computed tomography in all participants. Presence of CAC was defined as CACS >0.
Results When logistic regression analysis was performed with the presence of CAC as the dependent variable, the risk for CAC increased as BMI increased after adjusting for confounding variables (1.102 [95% confidence interval (CI), 1.000 to 1.216]; 1.284 [95% CI, 1.169 to 1.410]; in the overweight and obese groups vs. the normal weight group). When the participants were divided into six groups according to BMI and WC, the subjects with BMI and WC in the obese range showed the highest risk for CAC (1.321 [95% CI, 1.194 to 1.461]) and those with BMI in the overweight range and WC in the obese range showed the second highest risk for CAC (1.235 [95% CI, 1.194 to 1.461]).
Conclusion Participants with obesity defined by both BMI and WC showed the highest risk for CAC. Those with BMIs in the overweight range but with WC in the obese range showed the second highest risk for CAC, suggesting that WC as a marker of obesity is more predictive of CAC than BMI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship Between Blood Group and
Obesity Reduction Through Diet Among
Adults of Urban Bihar
Vidya, Rahul Singh
Journal of Health Management.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Coronary Artery Calcium Density and Volume With Predicted Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in South Asians: The Mediators of Atherosclerosis in South Asians Living in America (MASALA) Study
Mahmoud Al Rifai, Alka M. Kanaya, Namratha R Kandula, Jaideep Patel, Mouaz H. Al-Mallah, Matthew Budoff, Miguel Cainzos-Achirica, Michael H. Criqui, Salim S. Virani
Current Problems in Cardiology.2023; 48(4): 101105. CrossRef - Body weight at age 20 and in midlife is more important than weight gain for coronary atherosclerosis: Results from SCAPIS
Göran Bergström, Annika Rosengren, Elin Bacsovics Brolin, John Brandberg, Kerstin Cederlund, Gunnar Engström, Jan E. Engvall, Maria J. Eriksson, Isabel Gonçalves, Emil Hagström, Stefan K. James, Tomas Jernberg, Mikael Lilja, Martin Magnusson, Anders Perss
Atherosclerosis.2023; 373: 46. CrossRef - Weight gain with age and coronary atherosclerosis: Only the tip of a deadly iceberg
Isabelle Lemieux, Jean-Pierre Després
Atherosclerosis.2023; 373: 55. CrossRef - Central obesity and its associated factors among cancer patients at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia
Meseret Derbew Molla, Haileab Fekadu Wolde, Ephrem Tafesse Teferi, Anteneh Ayelign Kibret
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Added value of waist circumference to body mass index for predicting fracture risk in obesity: a prospective study from the CARTaGENE cohort
Anne-Frédérique Turcotte, Sonia Jean, Suzanne N. Morin, Fabrice Mac-Way, Claudia Gagnon
Archives of Osteoporosis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and significance of risk enhancing biomarkers in the United States population at intermediate risk for atherosclerotic disease
Gloria L. Vega, Jijia Wang, Scott M. Grundy
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2022; 16(1): 66. CrossRef - Pericardial fat, thoracic peri-aortic adipose tissue, and systemic inflammatory marker in nonalcoholic fatty liver and abdominal obesity phenotype
Chun-Ho Yun, Jing-Rong Jhuang, Meng-Ting Tsou
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Central Obesity and Associated Factors Among Urban Adults in Dire Dawa Administrative City, Eastern Ethiopia
Ephrem Israel, Kalkidan Hassen, Melese Markos, Kiber Wolde, Behailu Hawulte
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 601. CrossRef - Gender-Based Association of Coronary Artery Calcification and Framingham Risk Score With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Abdominal Obesity in Taiwanese Adults, a Cross-Sectional Study
Meng-Ting Tsou, Jau-Yuan Chen
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Joint Associations of Obesity and Cardiorespiratory Fitness With Coronary Artery Calcium Composition
Sae Young Jae, Hyun Jeong Kim, Kyung Hyun Lee, Setor K. Kunutsor, Kevin S. Heffernan, Yoon-Ho Choi, Mira Kang
Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation and Prevention.2022; 42(3): 202. CrossRef - Proposing new body mass index and waist circumference cut-offs based on cardiometabolic risks for a Central Asia population: A feasibility study
Aknur Kali, Arnur Gusmanov, Marat Aripov, Mei-Yen Chan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - New Model for Predicting the Presence of Coronary Artery Calcification
Samel Park, Min Hong, HwaMin Lee, Nam-jun Cho, Eun-Young Lee, Won-Young Lee, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyo-Wook Gil
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(3): 457. CrossRef - Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
Tiffany M. Powell-Wiley, Paul Poirier, Lora E. Burke, Jean-Pierre Després, Penny Gordon-Larsen, Carl J. Lavie, Scott A. Lear, Chiadi E. Ndumele, Ian J. Neeland, Prashanthan Sanders, Marie-Pierre St-Onge
Circulation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Obesity and Blood Pressure in Common Korean People
Nam Lyong Kang
Vascular Health and Risk Management.2021; Volume 17: 371. CrossRef - Prevalence of abdominal obesity and its association with cardiovascular risk among the adult population in Burkina Faso: findings from a nationwide cross-sectional study
Kadari Cisse, Sékou Samadoulougou, Mady Ouedraogo, Seni Kouanda, Fati Kirakoya-Samadoulougou
BMJ Open.2021; 11(7): e049496. CrossRef - Association between obesity and risk of fracture, bone mineral density and bone quality in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Anne-Frédérique Turcotte, Sarah O’Connor, Suzanne N. Morin, Jenna C. Gibbs, Bettina M. Willie, Sonia Jean, Claudia Gagnon, Tuan Van Nguyen
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0252487. CrossRef - Association of Body Weight Variability with Adverse Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease
Sang Heon Suh, Tae Ryom Oh, Hong Sang Choi, Chang Seong Kim, Eun Hui Bae, Sue K. Park, Yong-Soo Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Kyu Hun Choi, Kook-Hwan Oh, Seong Kwon Ma, Soo Wan Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(10): 3381. CrossRef - Associations among Obesity Degree, Glycemic Status, and Risk of Heart Failure in 9,720,220 Korean Adults
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 592. CrossRef - The effects of supplementation with L-arginine on anthropometric indices and body composition in overweight or obese subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Zeinali Khosroshahi, Omid Asbaghi, Sajjad Moradi, Mahnaz Rezaei kelishadi, Mojtaba Kaviani, Mahnaz Mardani, Cyrus Jalili
Journal of Functional Foods.2020; 71: 104022. CrossRef - Effect of Exercises and Diet Intervention in Pregnancy on Postpartum Weight Retention and Obesity Markers: Findings in Indian Women
Alka Pawalia, Sivachidambaram Kulandaivelan, Vikram Singh Yadav
Journal of Women's Health Physical Therapy.2020; 44(3): 123. CrossRef Magnitude of Central Obesity and its Associated Factors Among Adults in Urban Areas of Northwest Ethiopia
Meseret Derbew Molla, Haileab Fekadu Wolde, Asmamaw Atnafu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4169. CrossRef- Is the coronary artery calcium score the first-line tool for investigating patients with severe hypercholesterolemia?
Sandra Kutkienė, Žaneta Petrulionienė, Aleksandras Laucevičius, Rimantė Čerkauskienė, Vytautas Kasiulevičius, Artūras Samuilis, Virginija Augaitienė, Aurelija Gedminaitė, Gintarė Bieliauskienė, Akvilė Šaulytė-Mikulskienė, Justina Staigytė, Emilija Petruli
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Association of Z-Score of the Log-Transformed A Body Shape Index with Cardiovascular Disease in People Who Are Obese but Metabolically Healthy: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007-2010 (J Obes Metab Syndr 2018;27:158-65
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(2): 139. CrossRef - Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 461. CrossRef - Abdominal obesity increases metabolic risk factors in non-obese adults: a Hungarian cross-sectional study
Anita Lukács, Edina Horváth, Zsuzsanna Máté, Andrea Szabó, Katalin Virág, Magor Papp, János Sándor, Róza Ádány, Edit Paulik
BMC Public Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between thyroid hormone levels, body composition and insulin resistance in euthyroid subjects with normal thyroid ultrasound: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Hyemi Kwon, Jung‐Hwan Cho, Da Young Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol‐Young Park, Won‐Young Lee, Ki‐Won Oh, Sung‐Woo Park, Eun‐Jung Rhee
Clinical Endocrinology.2018; 89(5): 649. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Effects of lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, on adipose tissue remodeling and brown and beige adipose tissue development in db/db mice
G Kim, Y-h Lee, M R Yun, J-Y Lee, E G Shin, B-W Lee, E S Kang, B-S Cha
International Journal of Obesity.2018; 42(3): 542. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef
- Relationship Between Blood Group and
Obesity Reduction Through Diet Among
Adults of Urban Bihar

- Clinical Study
- Eligibility for Statin Treatment in Korean Subjects with Reduced Renal Function: An Observational Study
- Byung Sub Moon, Jongho Kim, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Se Eun Park, Hyung-Geun Oh, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Kyu-Beck Lee, Hyang Kim, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):402-409. Published online August 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.402
- 3,929 View
- 33 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between statin eligibility and the degree of renal dysfunction using the Adult Treatment Panel (ATP) III and the American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines in Korean adults.
Methods Renal function was assessed in 18,746 participants of the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study from January 2011 to December 2012. Subjects were divided into three groups according to estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR): stage 1, eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73 m2; stage 2, eGFR 60 to 89 mL/min/1.73 m2; and stages 3 to 5, eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Statin eligibility in these groups was determined using the ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, and the risk for 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was calculated using the Framingham Risk Score (FRS) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE).
Results There were 3,546 (18.9%) and 4,048 (21.5%) statin-eligible subjects according to ATP III and ACC/AHA guidelines, respectively. The proportion of statin-eligible subjects increased as renal function deteriorated. Statin eligibility by the ACC/AHA guidelines showed better agreement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) recommendations compared to the ATP III guidelines in subjects with stage 3 to 5 chronic kidney disease (CKD) (κ value, 0.689 vs. 0.531). When the 10-year ASCVD risk was assessed using the FRS and PCE, the mean risk calculated by both equations significantly increased as renal function declined.
Conclusions The proportion of statin-eligible subjects significantly increased according to worsening renal function in this Korean cohort. ACC/AHA guideline showed better agreement for statin eligibility with that recommended by KDIGO guideline compared to ATP III in subjects with CKD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Honghong Ren, Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yiting Wang, Junlin Zhang, Yucheng Wu, Rui Zhang, Tingli Wang, Jiali Wang, Yitao Zhu, Ruikun Guo, Huan Xu, Lin Li, Mark E. Cooper, Fang Liu
Renal Failure.2021; 43(1): 477. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef
- Association between atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk and renal outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus

- Clinical Study
- C-Peptide-Based Index Is More Related to Incident Type 2 Diabetes in Non-Diabetic Subjects than Insulin-Based Index
- Jong-Dai Kim, Sung Ju Kang, Min Kyung Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(2):320-327. Published online June 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.2.320
- 5,029 View
- 84 Download
- 45 Web of Science
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes can be efficiently prevented by life style modification and medical therapy. So, identification for high risk subjects for incident type 2 diabetes is important. The aim of this study is to identify the best β-cell function index to identify high risk subjects in non-diabetic Koreans.
Methods This is a retrospective longitudinal study. Total 140 non-diabetic subjects who underwent standard 2-hour 75 g oral glucose tolerance test from January 2007 to February 2007 at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital and followed up for more than 1 year were analyzed (mean follow-up, 54.9±16.4 months). The subjects were consist of subjects with normal glucose tolerance (
n =44) and subjects with prediabetes (n =97) who were 20 years of age or older. Samples for insulin and C-peptide levels were obtained at 0 and 30 minutes at baseline.Results Thirty subjects out of 140 subjects (21.4%) developed type 2 diabetes. When insulin-based index and C-peptide-based index are compared between progressor and non-progressor to diabetes, all C-peptide-based indices were statistically different between two groups, but only insulinogenic index and disposition index among insulin-based index were statistically different. C-peptide-based index had higher value of area under receiver operating characteristic curve (AROC) value than that of insulin-based index. "C-peptidogenic" index had highest AROC value among indices (AROC, 0.850; 95% confidence interval, 0.761 to 0.915). C-peptidogenic index had significantly higher AROC than insulinogenic index (0.850 vs. 0.731 respectively;
P =0.014).Conclusion C-peptide-based index was more closely related to incident type 2 diabetes in non-diabetic subjects than insulin-based index.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Atypical Diabetes: What Have We Learned and What Does the Future Hold?
Stephen I. Stone, Ashok Balasubramanyam, Jennifer E. Posey
Diabetes Care.2024; 47(5): 770. CrossRef - Insulinogenic index and early phase insulin secretion predict increased risk of worsening glucose tolerance and of cystic fibrosis-related diabetes
Kathryn J. Potter, Valérie Boudreau, Anne Bonhoure, François Tremblay, Annick Lavoie, Maité Carricart, Peter A. Senior, Rémi Rabasa-Lhoret
Journal of Cystic Fibrosis.2023; 22(1): 50. CrossRef - First-phase insulin secretion: can its evaluation direct therapeutic approaches?
Gianfranco Di Giuseppe, Gea Ciccarelli, Laura Soldovieri, Umberto Capece, Chiara M.A. Cefalo, Simona Moffa, Enrico C. Nista, Michela Brunetti, Francesca Cinti, Antonio Gasbarrini, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Andrea Giaccari, Teresa Mezza
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 34(4): 216. CrossRef - Insights on C-peptide in diabetes
Anuj Maheshwari
IP Journal of Nutrition, Metabolism and Health Science.2023; 6(2): 63. CrossRef - Human Milk Oligosaccharides in Maternal Serum Respond to Oral Glucose Load and Are Associated with Insulin Sensitivity
Marie-Therese Weiser-Fuchs, Elena Maggauer, Mireille N. M. van Poppel, Bence Csapo, Gernot Desoye, Harald C. Köfeler, Andrea Groselj-Strele, Slave Trajanoski, Herbert Fluhr, Barbara Obermayer-Pietsch, Evelyn Jantscher-Krenn
Nutrients.2023; 15(18): 4042. CrossRef - Elevated Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Level Associated With Decreasing Insulin Secretion May Forecast Memory Dysfunction in Patients With Long-Term Type 2 Diabetes
Xi Huang, Zuolin Xie, Chenchen Wang, Shaohua Wang
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Glycemic Outcomes at 1 Year Following Pediatric Total Pancreatectomy With Islet Autotransplantation
Sarah E. Swauger, Lindsey N. Hornung, Deborah A. Elder, Appakalai N. Balamurugan, David S. Vitale, Tom K. Lin, Jaimie D. Nathan, Maisam Abu-El-Haija
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(2): 295. CrossRef - Data-driven subgroups of type 2 diabetes, metabolic response, and renal risk profile after bariatric surgery: a retrospective cohort study
Violeta Raverdy, Ricardo V Cohen, Robert Caiazzo, Helene Verkindt, Tarissa Beatrice Zanata Petry, Camille Marciniak, Benjamin Legendre, Pierre Bauvin, Estelle Chatelain, Alain Duhamel, Elodie Drumez, Naima Oukhouya-Daoud, Mikael Chetboun, Gregory Baud, Em
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2022; 10(3): 167. CrossRef - The Relationship between the Lipid Accumulation Product and Beta-cell Function in Korean Adults with or without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Eun Cho, Seung Bum Yang, Mi Young Gi, Ju Ae Cha, so Young Park, Hyun Yoon
Endocrine Research.2022; 47(2): 80. CrossRef - Measures of Maternal Metabolic Health as Predictors of Severely Low Milk Production
Laurie A. Nommsen-Rivers, Erin A. Wagner, Dayna M. Roznowski, Sarah W. Riddle, Laura P. Ward, Amy Thompson
Breastfeeding Medicine.2022; 17(7): 566. CrossRef - Prediabetes: From diagnosis to prognosis
Teodora Beljić-Živković
Galenika Medical Journal.2022; 1(1): 57. CrossRef - C‐peptide determination in the diagnosis of type of diabetes and its management: A clinical perspective
Ernesto Maddaloni, Geremia B. Bolli, Brian M. Frier, Randie R. Little, Richard D. Leslie, Paolo Pozzilli, Raffaela Buzzetti
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 1912. CrossRef - Fasting Proinsulin Independently Predicts Incident Type 2 Diabetes in the General Population
Sara Sokooti, Wendy A. Dam, Tamas Szili-Torok, Jolein Gloerich, Alain J. van Gool, Adrian Post, Martin H. de Borst, Ron T. Gansevoort, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Robin P. F. Dullaart, Stephan J. L. Bakker
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1131. CrossRef - C-peptide is a predictor of telomere shortening: A five-year longitudinal study
Racha Ghoussaini, Hani Tamim, Martine Elbejjani, Maha Makki, Lara Nasreddine, Hussain Ismaeel, Mona P. Nasrallah, Nathalie K. Zgheib
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between early-pregnancy serum C-peptide and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a nested case–control study among Chinese women
Xue Yang, Yi Ye, Yi Wang, Ping Wu, Qi Lu, Yan Liu, Jiaying Yuan, Xingyue Song, Shijiao Yan, Xiaorong Qi, Yi-Xin Wang, Ying Wen, Gang Liu, Chuanzhu Lv, Chun-Xia Yang, An Pan, Jianli Zhang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Nutrition & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Human C-peptide is a ligand of the elastin-receptor-complex and therewith central to human vascular remodelling and disease in metabolic syndrome
Gert Wensvoort
Medical Hypotheses.2022; 168: 110964. CrossRef - Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DSM20174 Attenuates the Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Modulating Gut Microbiota, Improving Metabolic Risk Factors, and Attenuating Adipose Inflammation
José I. Riezu-Boj, Miguel Barajas, Tania Pérez-Sánchez, María J. Pajares, Miriam Araña, Fermín I. Milagro, Raquel Urtasun
Nutrients.2022; 14(24): 5212. CrossRef - Depression Augments Plasma APOA4 without Changes of Plasma Lipids and Glucose in Female Adolescents Carrying G Allele of APOA4 rs5104
Qi Wei Guo, Yan Jun Si, Yi Lin Shen, Xu Chen, Mei Yang, Ding Zhi Fang, Jia Lin
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience.2021; 71(10): 2060. CrossRef - Insulinemic and Inflammatory Dietary Patterns Show Enhanced Predictive Potential for Type 2 Diabetes Risk in Postmenopausal Women
Qi Jin, Ni Shi, Desmond Aroke, Dong Hoon Lee, Joshua J. Joseph, Macarius Donneyong, Darwin L. Conwell, Phil A. Hart, Xuehong Zhang, Steven K. Clinton, Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, Theodore M. Brasky, Rebecca Jackson, Lesley F. Tinker, Simin Liu, Lawrence S. P
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(3): 707. CrossRef - Analytical and clinical comparison between two different chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassays for the measurement of C-peptide in serum
Gian P. CAVIGLIA, Chiara ROSSO, Angelo ARMANDI, Davide G. RIBALDONE, Rinaldo PELLICANO, Elisabetta BUGIANESI
Minerva Biotechnology and Biomolecular Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pregnancy Serum DLK1 Concentrations Are Associated With Indices of Insulin Resistance and Secretion
Clive J Petry, Keith A Burling, Peter Barker, Ieuan A Hughes, Ken K Ong, David B Dunger
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(6): e2413. CrossRef - May C-peptide index be a new marker to predict proteinuria in anemic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Bilal Katipoglu, Mustafa Comoglu, Ihsan Ates, Nisbet Yilmaz, Dilek Berker
Endocrine Regulations.2020; 54(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between insulin resistance and risk of atrial fibrillation in non-diabetics
Yonggu Lee, Sung Joo Cha, Jung-Hwan Park, Jeong-Hun Shin, Young-Hyo Lim, Hwan-Cheol Park, Jinho Shin, Chun Ki Kim, Jin-Kyu Park
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2020; 27(18): 1934. CrossRef - Circulating levels of selected adipokines in women with gestational diabetes and type 2 diabetes
David Karasek, Ondrej Krystynik, Dominika Goldmannova, Lubica Cibickova, Jan Schovanek
Journal of Applied Biomedicine.2020; 18(2-3): 54. CrossRef - Search for clinical predictors of good glycemic control in patients starting or intensifying oral hypoglycemic pharmacological therapy: A multicenter prospective cohort study
Qian Ren, Li-Nong Ji, Ju-Ming Lu, Yu-Feng Li, Quan-Min Li, Shan-Shan Lin, Xiao-Feng Lv, Li Wang, Yuan Xu, Xiao-Hui Guo, Qi-Yu Guo, Li Ma, Jin Du, Ying-Li Chen, Cui-Ling Zhao, Qiu-Lan Zhang, Qi-Mei She, Xiu-Min Jiao, Mei-Hua Lu, Xiao-Meng Sun, Ying Gao, Ji
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(2): 107464. CrossRef - High Plasma Resistin Levels Portend the Insulin Resistance-Associated Susceptibility to Early Cognitive Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Chenchen Wang, Xi Huang, Sai Tian, Rong Huang, Dan Guo, Hongyan Lin, Jiaqi Wang, Shaohua Wang
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2020; 75(3): 807. CrossRef - Linearization of the Disposition Index equation allows evaluation of secretion-sensitivity coupling slopes
Kieren J. Mather, Melinda Chen, Tamara S. Hannon
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(7): 107589. CrossRef - Impact of interval walking training managed through smart mobile devices on albuminuria and leptin/adiponectin ratio in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jelizaveta Sokolovska, Karina Ostrovska, Leonora Pahirko, Gunita Varblane, Ksenija Krilatiha, Austris Cirulnieks, Inese Folkmane, Valdis Pirags, Janis Valeinis, Aija Klavina, Leo Selavo
Physiological Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Gender diversity of insulin sensitivity markers among patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus in northern India: A cross-sectional analytical study
Ravi Kant, Poonam Yadav, Surekha Kishore
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(7): 3315. CrossRef - Associations of Plasma BACE1 Level and BACE1 C786G Gene Polymorphism with Cognitive Functions in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross- Sectional Study
Sai Tian, Rong Huang, Dan Guo, Hongyan Lin, Jiaqi Wang, Ke An, Shaohua Wang
Current Alzheimer Research.2020; 17(4): 355. CrossRef - PPARGC1A Gene Promoter Methylation as a Biomarker of Insulin Secretion and Sensitivity in Response to Glucose Challenges
José L. Santos, Bernardo J. Krause, Luis Rodrigo Cataldo, Javier Vega, Francisca Salas-Pérez, Paula Mennickent, Raúl Gallegos, Fermín I. Milagro, Pedro Prieto-Hontoria, J. Ignacio Riezu-Boj, Carolina Bravo, Albert Salas-Huetos, Ana Arpón, José E. Galgani,
Nutrients.2020; 12(9): 2790. CrossRef - Plasma C-Peptide and Risk of Developing Type 2 Diabetes in the General Population
Sara Sokooti, Lyanne M. Kieneker, Martin H. de Borst, Anneke Muller Kobold, Jenny E. Kootstra-Ros, Jolein Gloerich, Alain J. van Gool, Hiddo J. Lambers Heerspink, Ron T Gansevoort, Robin P.F. Dullaart, Stephan J. L. Bakker
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(9): 3001. CrossRef Effect of Anthocyanins Supplementation on Serum IGFBP-4 Fragments and Glycemic Control in Patients with Fasting Hyperglycemia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Liping Yang, Zhaomin Liu, Wenhua Ling, Li Wang, Changyi Wang, Jianping Ma, Xiaolin Peng, Jianying Chen
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 3395. CrossRef- Adipose Mitochondrial Respiratory Capacity in Obesity is Impaired Independently of Glycemic Status of Tissue Donors
Britta Wessels, Julius Honecker, Theresa Schöttl, Lynne Stecher, Martin Klingenspor, Hans Hauner, Thomas Skurk
Obesity.2019; 27(5): 756. CrossRef - Higher Plasma Level of Nampt Presaging Memory Dysfunction in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment
Xi Huang, Chenchen Wang, Sai Tian, Rong Huang, Dan Guo, Haoqiang Zhang, Jijing Shi, Shaohua Wang
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2019; 70(1): 303. CrossRef - Increased Ratio of Global O-GlcNAcylation to Tau Phosphorylation at Thr212 Site Is Associated With Better Memory Function in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Rong Huang, Sai Tian, Jing Han, Rongrong Cai, Hongyan Lin, Dan Guo, Jiaqi Wang, Shaohua Wang
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Pancreatic fat content is associated with β-cell function and insulin resistance in Chinese type 2 diabetes subjects
Ting Lu, Yao Wang, Ting Dou, Bizhen Xue, Yuanyuan Tan, Jiao Yang
Endocrine Journal.2019; 66(3): 265. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Eriomin® in managing hyperglycemia and reversal of prediabetes condition: A double‐blind, randomized, controlled study
Carolina B. Ribeiro, Fernanda M. Ramos, John A. Manthey, Thais B. Cesar
Phytotherapy Research.2019; 33(7): 1921. CrossRef - Association between plasma adipsin level and mild cognitive impairment in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Dan Guo, Yang Yuan, Rong Huang, Sai Tian, Jiaqi Wang, Hongyan Lin, Ke An, Jin Han, Shaohua Wang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with intermediate hyperglycaemia
Bernd Richter, Bianca Hemmingsen, Maria-Inti Metzendorf, Yemisi Takwoingi
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - OGTT 1h serum C-peptide to plasma glucose concentration ratio is more related to beta cell function and diabetes mellitus
Hongmei Zhang, Bingxian Bian, Fan Hu, Qing Su
Oncotarget.2017; 8(31): 51786. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Obesity Influence on Insulin Activity and Resting Metabolic Rate in Type 2 Diabetes
Rodica Doros, Daniela Lixandru, Laura Petcu, Ariana Picu, Manuela Mitu, Janeta Tudosoiu, Constantin Ionescu-Tîrgoviste
Romanian Journal of Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases.2016; 23(4): 377. CrossRef - Insulin Secretory Capacity and Insulin Resistance in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Jong-Dai Kim, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(3): 354. CrossRef - Prediction of Diabetes Using Serum C-Peptide
Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(2): 275. CrossRef
- Atypical Diabetes: What Have We Learned and What Does the Future Hold?

- Clinical Study
- The Relationship between 10-Year Cardiovascular Risk Calculated Using the Pooled Cohort Equation and the Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Jeong In Lee, Min Chul Kim, Byung Sub Moon, Young Seok Song, Eun Na Han, Hyo Sun Lee, Yoonjeong Son, Jihyun Kim, Eun Jin Han, Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):86-92. Published online March 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.86
- 4,755 View
- 40 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the association between the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the estimated 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) calculated by Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE) and Framingham risk score (FRS).
Methods A total of 15,913 participants (mean age, 46.3 years) in a health screening program were selected for analysis. The presence and severity of fatty liver was assessed by abdominal ultrasonogram. Subjects who drank alcohol more than three times a week were excluded from the study.
Results Among the participants, 57.6% had no NAFLD, 35.4% had grade I, 6.5% had grade II, and 0.5% had grade III NAFLD. Mean estimated 10-year CVD risk was 2.59%, 3.93%, 4.68%, and 5.23% calculated using the PCE (
P for trend <0.01) and 4.55%, 6.39%, 7.33%, and 7.13% calculated using FRS, according to NAFLD severity from none to severe (P for trend <0.01). The odds ratio for ≥7.5% estimated CVD risk calculated using the PCE showed a higher correlation with increasing severity of NAFLD even after adjustment for conventional CVD risk factors (1.52, 2.56, 3.35 vs. the no NAFLD group as a reference,P <0.01) compared with calculated risk using FRS (1.65, 1.62, 1.72 vs. no NAFLD group as a reference,P <0.01).Conclusion In our study of apparently healthy Korean adults, increasing severity of NAFLD showed a higher correlation with estimated 10-year CVD risk when calculated using the PCE than when calculated using FRS.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Increases Cardiovascular Risk in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Dana Kablawi, Faisal Aljohani, Chiara Saroli Palumbo, Sophie Restellini, Alain Bitton, Gary Wild, Waqqas Afif, Peter L Lakatos, Talat Bessissow, Giada Sebastiani
Crohn's & Colitis 360.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low Relative Handgrip Strength Is Associated with a High Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Italian Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Samantha Maurotti, Roberta Pujia, Elisa Mazza, Maria Francesca Pileggi, Franco Arturi, Maria Grazia Tarsitano, Tiziana Montalcini, Arturo Pujia, Yvelise Ferro
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(22): 12489. CrossRef - Fatty Liver Disease: Diagnosis and Stratification
Yedidya Saiman, Andres Duarte-Rojo, Mary E. Rinella
Annual Review of Medicine.2022; 73(1): 529. CrossRef - “Dangerous liaisons: NAFLD and liver fibrosis increase cardiovascular risk in HIV”
Adriana Cervo, Giada Sebastiani, Jovana Milic, Thomas Krahn, Sergio Mazzola, Salvatore Petta, Antonio Cascio, Giovanni Guaraldi, Giovanni Mazzola
HIV Medicine.2022; 23(8): 911. CrossRef - Value of the triglyceride glucose index combined with body mass index in identifying non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Nong Li, Huiwen Tan, Aixia Xie, Cheng Li, Xuan Fu, Weiting Xang, Amina Kirim, Xuefang Huang
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Relation Between Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and the Risk of Coronary Heart Disease
Seyed Moayed Alavian, Hosein Zadi
Multidisciplinary Cardiovascular Annals.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk factors for cardiovascular disease among individuals with hepatic steatosis
Julia Karády, Maros Ferencik, Thomas Mayrhofer, Nandini M. Meyersohn, Daniel O. Bittner, Pedro V. Staziaki, Balint Szilveszter, Travis R. Hallett, Michael T. Lu, Stefan B. Puchner, Tracey G. Simon, Borek Foldyna, Geoffrey S. Ginsburg, Robert W. McGarrah,
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(12): 3406. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index and Related Parameters (Triglyceride Glucose-Body Mass Index and Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference) Identify Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Overweight/Obesity
Mohammad E. Khamseh, Mojtaba Malek, Rowshanak Abbasi, Hoda Taheri, Maryam Lahouti, Fariba Alaei-Shahmiri
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2021; 19(3): 167. CrossRef - Interplay between non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular risk in an asymptomatic general population
Grazia Pennisi, Vito Di Marco, Carola Buscemi, Giovanni Mazzola, Cristiana Randazzo, Federica Spatola, Antonio Craxì, Silvio Buscemi, Salvatore Petta
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2021; 36(9): 2389. CrossRef - Non-Laboratory-Based Simple Screening Model for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Developed Using Multi-Center Cohorts
Jiwon Kim, Minyoung Lee, Soo Yeon Kim, Ji-Hye Kim, Ji Sun Nam, Sung Wan Chun, Se Eun Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Joo Young Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 823. CrossRef - Coronary Artery Disease is More Severe in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis than Fatty Liver
Toshihiro Niikura, Kento Imajo, Anna Ozaki, Takashi Kobayashi, Michihiro Iwaki, Yasushi Honda, Takaomi Kessoku, Yuji Ogawa, Masato Yoneda, Hiroyuki Kirikoshi, Satoru Saito, Atsushi Nakajima
Diagnostics.2020; 10(3): 129. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Disease in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Screening and Management
Hersh Shroff, Lisa B. VanWagner
Current Hepatology Reports.2020; 19(3): 315. CrossRef - Triglyceride Glucose Index Is Superior to the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance for Predicting Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Korean Adults
Sang Bae Lee, Min Kyung Kim, Shinae Kang, Kahui Park, Jung Hye Kim, Su Jung Baik, Ji Sun Nam, Chul Woo Ahn, Jong Suk Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(2): 179. CrossRef - Mortality Risk Detected by Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Score in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Pegah Golabi, Natsu Fukui, James Paik, Mehmet Sayiner, Alita Mishra, Zobair M. Younossi
Hepatology Communications.2019; 3(8): 1050. CrossRef - Lower hand grip strength in older adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a nationwide population-based study
Beom-Jun Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, Seung Hun Lee, Seongbin Hong, Mark W. Hamrick, Carlos M. Isales, Jung-Min Koh
Aging.2019; 11(13): 4547. CrossRef - Implication of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Metabolic Syndrome, and Subclinical Inflammation on Mild Renal Insufficiency
Ga Eun Nam, Soon Young Hwang, Hye Soo Chung, Ju Hee Choi, Hyun Jung Lee, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Implication of liver enzymes on incident cardiovascular diseases and mortality: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyung Mook Choi, Kyungdo Han, Sanghyun Park, Hye Soo Chung, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Seon Mee Kim
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Controlled Attenuation Parameter as a Noninvasive Method to Detect and Quantify Hepatic Steatosis in Chronic Liver Disease: What Is the Clinical Relevance
Mariana Verdelho Machado
GE - Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2017; 24(4): 157. CrossRef - Effect of statin on hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide nested case‐control study
Gyuri Kim, Suk‐Yong Jang, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Se‐young Park, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
International Journal of Cancer.2017; 140(4): 798. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on Analyses from the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(2): 81. CrossRef - Increased risk for development of coronary artery calcification in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and systemic inflammation
Jihyun Kim, Da Young Lee, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Susanne Kaser
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(7): e0180118. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Emerging Burden in Cardiometabolic and Renal Diseases
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 430. CrossRef
- Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Increases Cardiovascular Risk in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases

- Clinical Study
- Association of Waist-Height Ratio with Diabetes Risk: A 4-Year Longitudinal Retrospective Study
- Yoon Jeong Son, Jihyun Kim, Hye-Jeong Park, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):127-133. Published online March 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.127
- 4,356 View
- 37 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 24 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) is an easy and inexpensive adiposity index that reflects central obesity. In this study, we examined the association of various baseline adiposity indices, including WHtR, with the development of diabetes over 4 years of follow-up in apparently healthy Korean individuals.
Methods A total of 2,900 nondiabetic participants (mean age, 44.3 years; 2,078 men) in a health screening program, who repeated the medical check-up in 2005 and 2009, were recruited. Subjects were divided into two groups according to development of diabetes after 4 years. The cut-off values of baseline body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC), and WHtR for the development of diabetes over 4 years were calculated. The sensitivity, specificity, and mean area under the receiver operator characteristic curve (AUROC) of each index were assessed. The odds ratio (OR) for diabetes development was analyzed for each of the three baseline adiposity indices.
Results During the follow-up period, 101 new cases (3.5%) of diabetes were diagnosed. The cut-off WHtR value for diabetes development was 0.51. Moreover, WHtR had the highest AUROC value for diabetes development among the three adiposity indices (0.716, 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.669 to 0.763; 0.702, 95% CI, 0.655 to 0.750 for WC; 0.700, 95% CI, 0.651 to 0.750 for BMI). After adjusting for confounding variables, the ORs of WHtR and WC for diabetes development were 1.95 (95% CI, 1.14 to 3.34) and 1.96 (95% CI, 1.10 to 3.49), respectively. No significant differences were observed between the two groups regarding BMI.
Conclusion Increased baseline WHtR and WC correlated with the development of diabetes after 4 years. WHtR might be a useful screening measurement to identify individuals at high risk for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of waist circumference and waist‐to‐height ratio as predictors of clustering of cardiovascular risk factors among middle‐aged people in rural Khanh Hoa, Vietnam
Rachana Manandhar Shrestha, Thuy Thi Phuong Pham, Shohei Yamamoto, Chau Que Nguyen, Ami Fukunaga, Phan Cong Danh, Masahiko Hachiya, Huy Xuan Le, Hung Thai Do, Tetsuya Mizoue, Yosuke Inoue
American Journal of Human Biology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel anthropometric indices for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus
Erfan Sadeghi, Alireza Khodadadiyan, Seyed Ali Hosseini, Sayed Mohsen Hosseini, Ashraf Aminorroaya, Massoud Amini, Sara Javadi
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition and Cardiovascular Risk: A Study of Polish Military Flying Personnel
Agata Gaździńska, Stefan Gaździński, Paweł Jagielski, Paweł Kler
Metabolites.2023; 13(10): 1102. CrossRef - Cues of pregnancy decrease female physical attractiveness for males
Pavol Prokop, Martina Zvaríková, Milan Zvarík, Peter Fedor
Current Psychology.2022; 41(2): 697. CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio has a stronger association with cardiovascular risks than waist circumference, waist-hip ratio and body mass index in type 2 diabetes
Jiang-Feng Ke, Jun-Wei Wang, Jun-Xi Lu, Zhi-Hui Zhang, Yun Liu, Lian-Xi Li
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 183: 109151. CrossRef - Diagnostic accuracy of anthropometric indices for discriminating elevated blood pressure in pediatric population: a systematic review and a meta-analysis
Jun-Min Tao, Wei Wei, Xiao-Yang Ma, Ying-Xiang Huo, Meng-Die Hu, Xiao-Feng Li, Xin Chen
BMC Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The utilization of BMI in patients with high WHtR as to cardiovascular risk
Meliha Melin UYGUR
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(4): 1133. CrossRef - Assessment of obesity indices for prediction of hyperglycemia in adult population of Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh), India
Neha Rai, Hanjabam Barun Sharma, Renu Kumari, Jyotsna Kailashiya
Indian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2021; 64: 195. CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio and metabolic phenotype compared to the Matsuda index for the prediction of insulin resistance
Katharina Lechner, Benjamin Lechner, Alexander Crispin, Peter E. H. Schwarz, Helene von Bibra
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Waist-to-Height Ratio (WHtR) in Predicting Coronary Artery Disease Compared to Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference in a Single Center from Saudi Arabia
Mostafa Q. Alshamiri, Faisal Mohd A Habbab, Saad Saeed AL-Qahtani, Khalil Abdullah Alghalayini, Omar Mohammed Al-Qattan, Fayez El-shaer, Anne Knowlton
Cardiology Research and Practice.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - A simple cut-off for waist-to-height ratio (0·5) can act as an indicator for cardiometabolic risk: recent data from adults in the Health Survey for England
Sigrid Gibson, Margaret Ashwell
British Journal of Nutrition.2020; 123(6): 681. CrossRef - Glucose Levels as a Mediator of the Detrimental Effect of Abdominal Obesity on Relative Handgrip Strength in Older Adults
Miguel Ángel Pérez-Sousa, Jesús del Pozo-Cruz, Carlos A. Cano-Gutiérrez, Atilio J. Ferrebuz, Carolina Sandoval-Cuellar, Mikel Izquierdo, Paula A. Hernández-Quiñonez, Robinson Ramírez-Vélez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(8): 2323. CrossRef Abnormal Glucose Metabolism and Associated Risk Factors Among Adults in Mekelle City, Ethiopia
Gebremedhin Gebreegziabiher, Tefera Belachew, Dessalegn Tamiru
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4017. CrossRefAnthropometric Indexes for Predicting High Blood Pressure in Vietnamese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
Quan Nguyen Minh, Minh Hoang Nguyen Vo
Integrated Blood Pressure Control.2020; Volume 13: 181. CrossRef- Relation between Baseline Height and New Diabetes Development: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se-Eun Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Won-Young Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 794. CrossRef - Issues in Measuring and Interpreting Diet and Its Contribution to Obesity
Rachael M. Taylor, Rebecca L. Haslam, Tracy L. Burrows, Kerith R. Duncanson, Lee M. Ashton, Megan E. Rollo, Vanessa A. Shrewsbury, Tracy L. Schumacher, Clare E. Collins
Current Obesity Reports.2019; 8(2): 53. CrossRef - Assessment of the validity of multiple obesity indices compared with obesity-related co-morbidities
Jaeeun Myung, Kyung Yoon Jung, Tae Hyun Kim, Euna Han
Public Health Nutrition.2019; : 1. CrossRef - Profiles of body mass index and blood pressure among young adults categorised by waist-to-height ratio cut-offs in Shandong, China
Ying-xiu Zhang, Shu-rong Wang
Annals of Human Biology.2019; 46(5): 409. CrossRef - Air Pollution Has a Significant Negative Impact on Intentional Efforts to Lose Weight: A Global Scale Analysis
Morena Ustulin, So Young Park, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(4): 320. CrossRef - Being Metabolically Healthy, the Most Responsible Factor for Vascular Health
Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 19. CrossRef - Waist-to-height ratio index for predicting incidences of hypertension: the ARIRANG study
Jung Ran Choi, Sang Baek Koh, Eunhee Choi
BMC Public Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of various anthropometric indices for the identification of a predictor of incident hypertension: the ARIRANG study
J. R. Choi, S. V. Ahn, J. Y. Kim, S. B. Koh, E. H. Choi, G. Y. Lee, Y. E. Jang
Journal of Human Hypertension.2018; 32(4): 294. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - THE ASSESMENT OF RELATION BETWEEN WAIST/HEIGHT RATIO AND TYPE 2 DIABETES RISK AMONG NURSING STUDENTS
Ceren Gezer
Journal of Food and Health Science.2017; : 141. CrossRef
- Comparison of waist circumference and waist‐to‐height ratio as predictors of clustering of cardiovascular risk factors among middle‐aged people in rural Khanh Hoa, Vietnam

- Clinical Study
- Effect of Pitavastatin Treatment on ApoB-48 and Lp-PLA2 in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: Substudy of PROspective Comparative Clinical Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of PITavastatin in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- Hyo-Sun Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Sung Rae Kim, Hak Chul Jang, Cheol-Young Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(1):120-126. Published online March 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.1.120
- 3,487 View
- 35 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Apolipoprotein (Apo) B-48 is an intestinally derived lipoprotein that is expected to be a marker for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is a vascular-specific inflammatory marker and important risk predictor of CVD. The aim of this study was to explore the effect of pitavastatin treatment and life style modification (LSM) on ApoB-48 and Lp-PLA2 levels in metabolic syndrome (MS) patients at relatively low risk for CVD, as a sub-analysis of a previous multi-center prospective study.
Methods We enrolled 75 patients with MS from the PROPIT study and randomized them into two treatment groups: 2 mg pitavastatin daily+intensive LSM or intensive LSM only. We measured the change of lipid profiles, ApoB-48 and Lp-PLA2 for 48 weeks.
Results Total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol, non-high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and ApoB-100/A1 ratio were significantly improved in the pitavastatin+LSM group compared to the LSM only group (
P ≤0.001). Pitavastatin+LSM did not change the level of ApoB-48 in subjects overall, but the level of ApoB-48 was significantly lower in the higher mean baseline value group of ApoB-48. The change in Lp-PLA2 was not significant after intervention in either group after treatment with pitavastatin for 1 year.Conclusion Pitavastatin treatment and LSM significantly improved lipid profiles, ApoB-100/A1 ratio, and reduced ApoB-48 levels in the higher mean baseline value group of ApoB-48, but did not significantly alter the Lp-PLA2 levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comprehensive review on the lipid and pleiotropic effects of pitavastatin
Amirhossein Sahebkar, Nasim Kiaie, Armita Mahdavi Gorabi, Massimo R. Mannarino, Vanessa Bianconi, Tannaz Jamialahmadi, Matteo Pirro, Maciej Banach
Progress in Lipid Research.2021; 84: 101127. CrossRef - Change in ALT levels after administration of HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitors to subjects with pretreatment levels three times the upper normal limit in clinical practice
Hyunah Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Hun‐Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Use of Moderate‐Intensity Statins for Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level above 190 mg/dL at Baseline in Koreans
Hun‐Sung Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Sue Hyun Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Sun Jung Baik, Hyunah Kim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In‐Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Ju Han Kim
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2017; 121(4): 272. CrossRef - Another statin option in HIV
Philip E Tarr, Helen Kovari
The Lancet HIV.2017; 4(7): e278. CrossRef - Clinical benefits of pitavastatin: focus on patients with diabetes or at risk of developing diabetes
Vivencio Barrios, Carlos Escobar
Future Cardiology.2016; 12(4): 449. CrossRef
- A comprehensive review on the lipid and pleiotropic effects of pitavastatin


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



